The convergence between Geographic Information Modeling (GIS) and Building Information Modeling (BIM) marks a significant milestone in project and infrastructure management. As technologies evolve, the initial integration of these two complex systems opens doors to a more holistic and efficient approach in the design, construction, and management of buildings and infrastructure. In this post, we will explore the foundations of this integration, the challenges faced, and the emerging opportunities that promise to revolutionize the construction industry and urban planning.
What is Geographic Information Modeling (GIS)?
Geographic Information Modeling (GIS), also known as Geographic Information System (GIS), is a technology that enables the capture, storage, manipulation, analysis, and presentation of geospatial data. This data refers to information about the Earth’s surface and its features, such as topography, terrain, land use, natural resources, infrastructure, among others. GIS integrates geographic data with attribute information, providing a visual and analytical representation of the real world. This allows users to understand spatial patterns, make informed decisions, and solve complex problems in a wide range of fields, including urban planning, environmental management, agriculture, transportation, telecommunications, and many others.

Benefits of Using GIS
Among the benefits that the use of GIS can provide, we will mention 5 that we consider most relevant:
1. Informed decision-making: GIS provides a platform for analyzing and visualizing geospatial data, allowing users to make decisions based on accurate and contextualized information.
2. Efficient planning: By integrating geographic data and attributes, GIS facilitates the planning and management of natural resources, urban infrastructure, transportation, public utilities, and other activities, helping to optimize resource utilization and reduce costs.
3. Advanced spatial analysis: GIS enables the performance of complex spatial analyses, such as surface modeling, proximity analysis, spatial interpolation, and network modeling, offering valuable insights for environmental, urban, and engineering problems.
4. Monitoring and control: With GIS, it is possible to monitor changes over time in areas such as land use, vegetation cover, pollution levels, and movement patterns, facilitating trend tracking, impact assessment, and implementation of corrective measures.
5. Effective communication: GIS allows the creation of intuitive maps and visualizations that can be easily shared and understood by different stakeholders, improving communication and collaboration in multidisciplinary projects and planning initiatives.
How Does GIS Integrate with BIM?
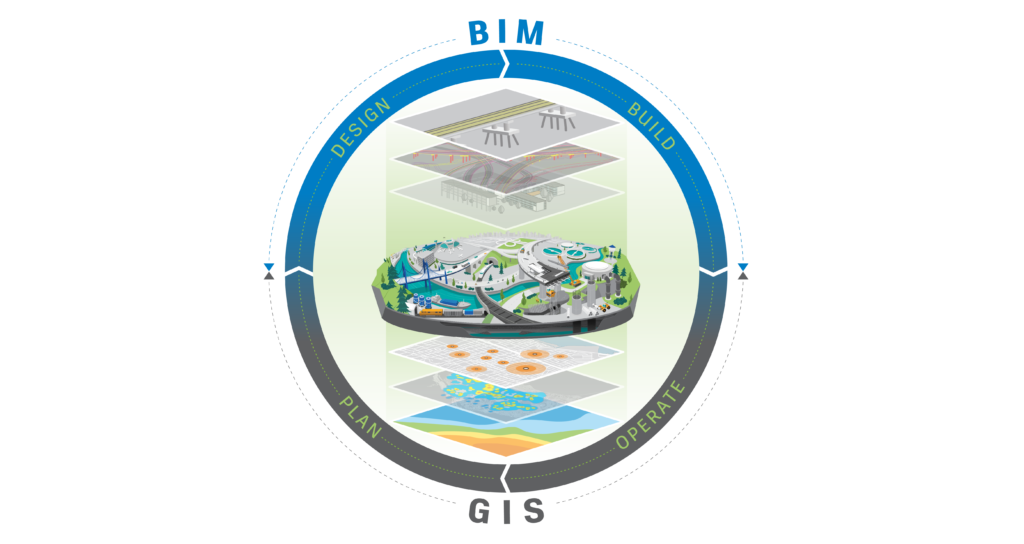
The integration between Geographic Information System (GIS) and Building Information Modeling (BIM) is becoming increasingly relevant in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. Among the possible integration methods, we decided to mention 5 that we consider important:
1. BIM Project Geolocation: GIS can provide accurate geospatial information about the location where a BIM project will be implemented, helping professionals to better understand the environmental, topographic, and infrastructural context.
2. Site Analysis and Urban Planning: GIS can be used to conduct site analysis and urban planning, providing data on land use, zoning, existing infrastructure, transportation networks, among others, which can be integrated into BIM models for a more comprehensive and informed decision-making.
3. Asset and Infrastructure Management: GIS is widely used for managing assets and existing infrastructure, such as utilities networks, roads, bridges, and transportation systems. Integrating this data with BIM models can improve efficiency in infrastructure maintenance, operation, and planning.
4. Visualization of Spatial Data in BIM Models: Integrating GIS with BIM allows the visualization of spatial data directly in BIM models, providing a more complete understanding of the built environment and facilitating communication between different stakeholders.
5. Simulation and Risk Analysis: GIS can provide data for simulations of natural risks, such as floods, landslides, and forest fires, which can be integrated into BIM models to assess and mitigate risks in construction and infrastructure projects.
Integrating GIS and BIM – Paving the Way for the Future of Construction
Having explored the initial integration between Geographic Information Modeling (GIS) and Building Information Modeling (BIM), the transformative potential of this convergence for the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry becomes evident. The ability to combine detailed geospatial data with accurate building information opens up new possibilities for a more holistic and informed approach in project and infrastructure development.
As we move forward, it is essential to recognize the importance of further deepening this integration, especially in our next topic, where we will address the understanding of terrain modeling fundamentals and its integration with BIM.




Deixe um comentário