Choosing the appropriate BIM software is crucial for the success and efficiency of infrastructure projects, and that’s exactly what we will explore in this initial guide. With the growth of digitization in civil engineering, careful selection of BIM software becomes a key component in optimizing processes, collaboration, and accuracy in infrastructure project management.
What should I consider when choosing the right software?
First and foremost, it is essential to assess the specific needs of the project, considering the complexity of the infrastructure, team size, and ultimate goals. Additionally, it’s important to check the software’s interoperability, ensuring compatibility with other tools used in the industry. Evaluating the software’s collaboration and communication capabilities is also crucial, as effective integration among team members is vital for the smooth progress of the project. Consider the scalability of the software, regular updates, and technical support provided by the developing company. By conducting a comprehensive analysis of these factors, professionals can make an informed decision and choose the BIM software that best meets the specific needs of their infrastructure projects. Below, we will separately address each of these cases.
Project-Specific Needs
When choosing BIM software for infrastructure projects, it is fundamental to consider the specific needs of the project, as each venture has unique requirements. First and foremost, evaluate the complexity of the infrastructure at hand.
More complex projects, such as large railways, bridges, or public transportation systems, may require robust software capable of handling detailed modeling and advanced analysis.
In this context, we outline below some specificities and which software may be suitable for them in terms of advanced modeling and analysis, and the justifications for their use.
Railway Projects
1 – Bentley OpenRail: Bentley OpenRail is a specialized solution for advanced railway modeling, offering specific tools for precise design of tracks, stations, and other elements related to railway systems.

2 – AutoCAD Civil 3D (Autodesk): AutoCAD Civil 3D provides advanced features for railway modeling and design, allowing the creation of detailed alignments, profiles, and cross-sections.
Road Projects
1 – AutoCAD Civil 3D (Autodesk): Autodesk’s Civil 3D is widely used for advanced modeling in road projects, offering specific features for geometric design, surface analysis, and highway-related data management.
2 – OpenRoads (Bentley): Bentley’s OpenRoads is a robust tool for advanced modeling in road projects, offering specific functionalities for geometry design, drainage, and pavement design.

Bridge Projects
1 – AutoCAD Civil 3D (Autodesk): Civil 3D, from Autodesk, is a widely employed tool for BIM modeling of bridges. It offers specific features for geometric design, surface analysis, and highway and bridge-related data management.
2 – Bentley OpenBridge Modeler: Developed by Bentley, OpenBridge Modeler is a specialized solution for BIM modeling of bridges. It allows the creation of detailed 3D models, facilitating design and structural analysis.
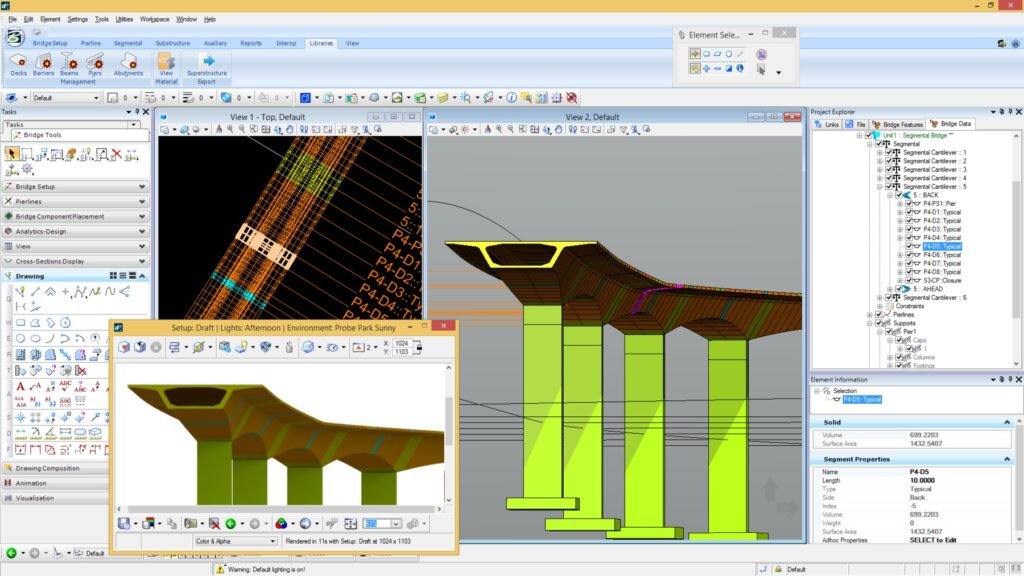
3 – SAP2000 (Computers and Structures, Inc.): SAP2000 is widely used for advanced structural analyses, including bridges. It provides robust features for modeling, simulation, and precise sizing of different types of bridges.
Topography Projects
1 – AutoCAD Civil 3D (Autodesk): Civil 3D enables the creation of dynamic 3D models, offering a precise visual representation of the terrain. This is crucial for topography projects, where three-dimensional visualization is essential for understanding the layout and compliance of the terrain. The tool has specific features for topography, such as creating topographic surfaces, elevation analysis, generating contour lines, and efficient handling of terrain-related data.

2 – Trimble Business Center: Trimble Business Center is a comprehensive solution for advanced modeling in topography, offering tools for field data processing, surface creation, and detailed topographic model generation.
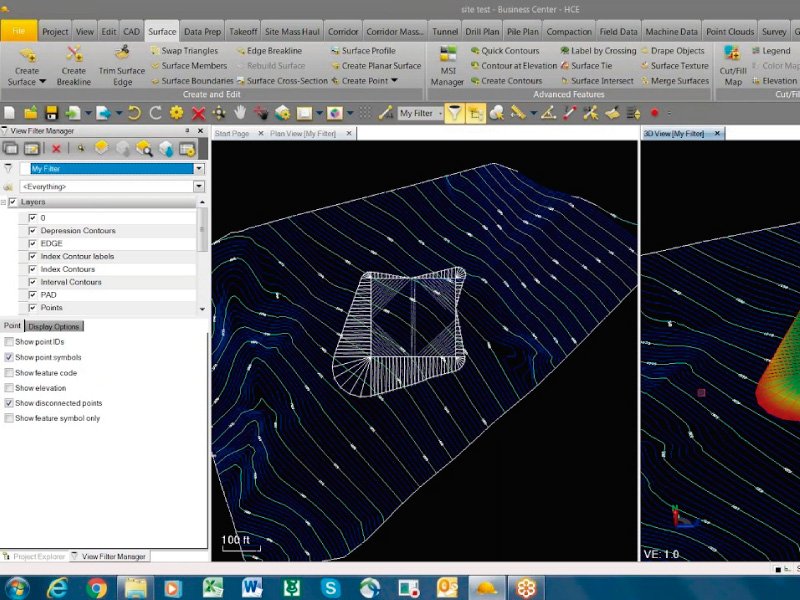
3 – Global Mapper (Blue Marble Geographics): Global Mapper is a versatile tool that allows advanced modeling in topography, offering functionalities for data processing, creation of digital elevation models, and three-dimensional visualization.
Drainage Projects
1 – SWMM (Storm Water Management Model – U.S. Environmental Protection Agency): SWMM is a specialized tool for advanced modeling of drainage systems, allowing detailed simulation of water flows in urban and rural drainage networks.
2 – InfoSWMM (Innovyze): InfoSWMM is an advanced solution for modeling drainage systems, offering detailed capabilities for hydraulic simulation and analysis of water flow networks.
Airport Projects
1 – Autodesk InfraWorks: Autodesk InfraWorks is a BIM tool that allows the creation of comprehensive 3D models for infrastructure planning and design. It is often used in airport projects due to its ability to integrate geospatial data, create realistic visualizations, and facilitate collaboration among multidisciplinary teams.
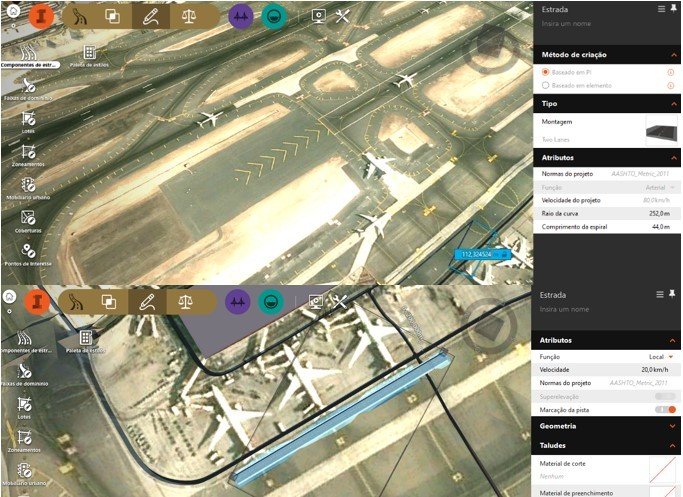
2 – Bentley OpenBuildings: Bentley OpenBuildings is a Bentley Systems BIM platform that supports advanced modeling of infrastructure projects, including airports. It offers specific tools for designing terminals, runways, hangars, and other airport facilities, as well as features for analysis and simulation.
Software Interoperability
When choosing BIM software for infrastructure projects, interoperability is an important factor to consider. The software’s ability to efficiently integrate with other tools and data formats used throughout the project’s lifecycle is essential to ensure an integrated workflow. Infrastructure projects involve various disciplines, and interoperability enables efficient collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, facilitating data exchange and ensuring consistency throughout the project.
Additionally, interoperability is crucial for the efficient integration of geospatial data, common in infrastructure projects. The ability to incorporate topographical and location information contributes to creating more accurate BIM models aligned with the physical environment. Choosing software that incorporates industry standards is also fundamental, ensuring that the generated data can be understood by other tools and systems used in the industry, facilitating communication and information exchange with stakeholders.
Software Collaboration and Communication Capabilities
The collaboration and communication capabilities of BIM software are elements to consider when choosing a solution for infrastructure projects. In multidisciplinary environments where various teams contribute to the project, efficient collaboration becomes crucial. The presence of a centralized data environment, integrated comment and annotation tools, and the ability for remote access and online collaboration are essential aspects to ensure that all team members can work in a coordinated manner and access the latest information in real time.
Integration with external communication tools, such as emails and video conferences, is also important for effective communication. Additionally, version control and the history of changes in the BIM model ensure traceability of decisions made throughout the project, contributing to transparent communication. The availability of training and technical support is an additional component that ensures the team is properly equipped to use the collaboration features of the software, minimizing obstacles and promoting effective project execution.
Software Scalability, Updates, and Technical Support
Scalability refers to the software’s ability to handle projects of different sizes and complexities. When choosing BIM software, it is crucial to consider whether it can scale efficiently to meet the growing demands of the project. Infrastructure projects often evolve in scale and complexity as they progress, and scalable software is essential to support these changes without compromising performance.
The constant evolution of technology and changes in industry needs demand regular updates to BIM software. Choosing software with frequent updates ensures that the platform aligns with the latest trends, standards, and industry requirements. This ensures that users have access to enhanced features, bug fixes, and continuous support for technological innovations.
Technical support plays a crucial role in problem resolution, providing guidance and ensuring that the team can efficiently use all the software’s features. When choosing BIM software, it’s important to assess the quality and readiness of the technical support offered by the developing company. Effective technical support minimizes workflow disruptions, reducing the impact of potential technical issues.
From Choosing BIM Software to Inspiration
In summary, choosing BIM software for infrastructure projects is a strategic decision that directly impacts the efficiency and success of the venture. By considering interoperability, collaboration capabilities, scalability, updates, and technical support, professionals can make informed decisions that meet the specific demands of their projects. In our next post, we will seek to illustrate the content we are addressing through some Success Stories in BIM Projects for Infrastructure.
The analysis of practical cases serves to inspire and provide valuable insights for project teams, which were essential for the success of the analyzed cases. Additionally, it assists us in our day-to-day efforts to achieve successful outcomes in our own BIM-based infrastructure projects.




Deixe um comentário