Automating processes in Building Information Modeling (BIM) can be an exciting journey, but before we delve into specific tools, it’s important to know that certain knowledge is considered fundamental to ensure the best results from the automation process. In this article, we will explore some of the key automation tools in BIM, providing an overview for beginners interested in enhancing their knowledge in this area.
Fundamental Knowledge for BIM Automation
Programming: Understanding the basics of programming facilitates the creation of scripts and task automation, with languages such as Python, C# (for Dynamo), and GDL (Geometric Description Language) being useful.
Parametric Modeling: Understanding how to create parametric models is essential, including defining parameters, relationships, and logic to ensure model flexibility.
BIM Concepts: Having a solid understanding of BIM principles, covering 3D modeling, interoperability, project coordination, and team collaboration.
Tools Used in Different BIM Processes
1. Geometric Modeling
Revit: A powerful BIM tool that automates geometric modeling through parametric objects. The process is guided by parameter and rule definitions, allowing architectural, structural, and MEP elements to be generated automatically from an initial set of data. This parametric approach not only accelerates the creation of complex 3D models but also maintains project consistency and integrity throughout phases.

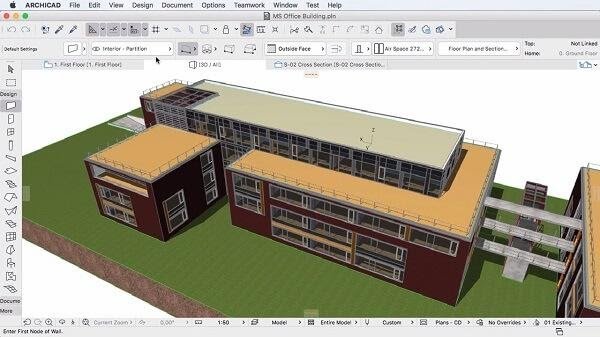
ArchiCAD: Uses parametric objects and automation to create integrated 3D models. With an information-based approach, the tool allows users to develop architectural elements efficiently. ArchiCAD’s automation is evident in its ability to automatically update the model when changes occur, maintaining consistency across different parts of the project.
SketchUp: While known for its intuitive interface, SketchUp can be automated through scripts for efficient geometric modeling. Scripts enable the creation of complex shapes and the application of repetitive patterns, streamlining tasks that would otherwise be labor-intensive. This flexibility makes SketchUp a versatile tool for various modeling needs.

Allplan: Offers automation in parametric and intelligent creation of 3D models. Its parametric approach allows the definition of relationships between elements, facilitating automatic updates when changes occur. With automation, modeling becomes faster and more efficient, ensuring model consistency throughout the project lifecycle.
Rhino: Although known for its modeling flexibility, it can be automated through scripts and plugins. This automation capability allows advanced parametric modeling, where algorithms and design logic can be applied to efficiently create complex shapes. Rhino’s interoperability also facilitates integration with other BIM workflow tools.

2. Material Quantification and Automated Budgeting
Navisworks: Automates material quantification through interference detection and automatic extraction of quantities from the model. By analyzing the BIM model, the tool automatically identifies collisions between elements and generates accurate material lists, providing a solid basis for detailed budgets.
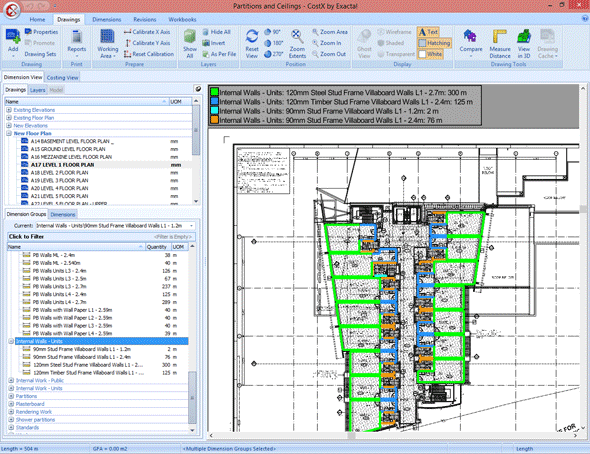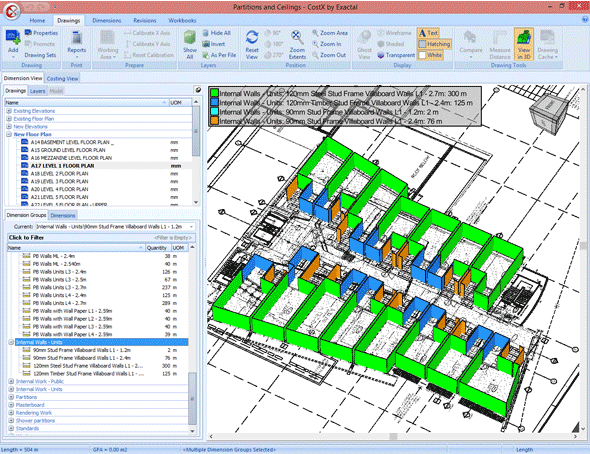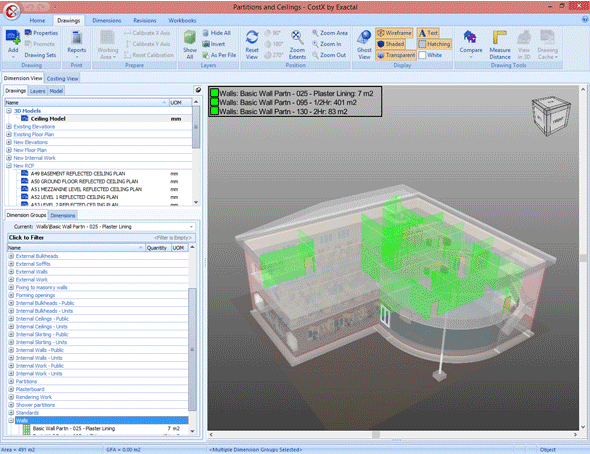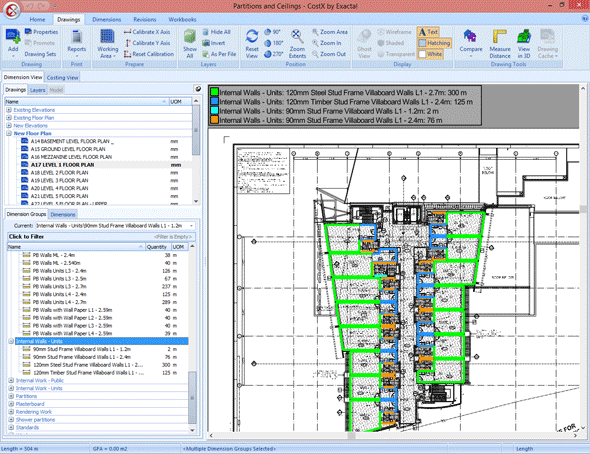
CostX: Automates the extraction of data from the BIM model to generate accurate material lists and construction budgets. The tool offers intelligent recognition features, allowing automatic identification of components and association with specific costs, resulting in faster and more accurate estimates.
Revit (Schedule): Automatic generation of material and cost lists is possible through parametric schedules. These schedules automatically extract specific information from the model, such as material quantities, areas, and volumes, creating a detailed basis for cost estimates.

BIM 360 Cost Management: Integrates with BIM models to automate cost estimation and manage construction budgets. By directly connecting cost data to the model, the tool ensures a consistent and real-time view of the project’s financial status.

Assemble: The tool offers automation in extracting data from the BIM model for cost analysis and material quantification. Its ability to filter specific information allows users to focus on relevant elements, streamlining the creation of budgets and estimates.
Automated Coordination and Collaboration
BIM 360: Automates real-time coordination, providing a centralized platform for efficient collaboration. Its ability to automatically synchronize between project participants ensures that all updates to the model are instantly reflected, reducing conflicts and rework.
Tekla BIMsight: Facilitates automatic detection of interferences and coordination between disciplines. Automation in collision identification and issue communication speeds up the resolution process, improving collaboration between teams.

Solibri Model Checker: Automatically verifies compliance, detecting and resolving coordination issues in the BIM model. Its automation in identifying conflicts and errors ensures that the project complies with established standards and regulations.
ClashMEP: Automates the identification of conflicts in MEP installations. By automatically analyzing the model, the tool highlights areas with interferences, allowing quick and efficient resolution.

Autodesk Collaborate: Offers automation in collaboration, ensuring the automatic synchronization of model updates between involved parties. This provides a unified view of the project and facilitates communication between distributed teams.
Structural Analysis and Simulation
Robot Structural Analysis: Automatically performs advanced structural analysis. Using finite element methods, the tool calculates stresses, deformations, and other structural characteristics automatically, optimizing the sizing process.

ETABS: Automates structural modeling and analysis, providing fast and accurate results. Its automation in applying loads and generating load combinations simplifies complex engineering tasks.

SAP2000: SAP2000 offers automation in structural analysis, allowing automatic adjustments to the design based on analysis results. Its parametric approach facilitates rapid and efficient iteration during the design process.
Dlubal RFEM: Uses automation for efficient structural analysis and design. The tool integrates with the BIM model, allowing the automatic transfer of relevant data for structural analysis.
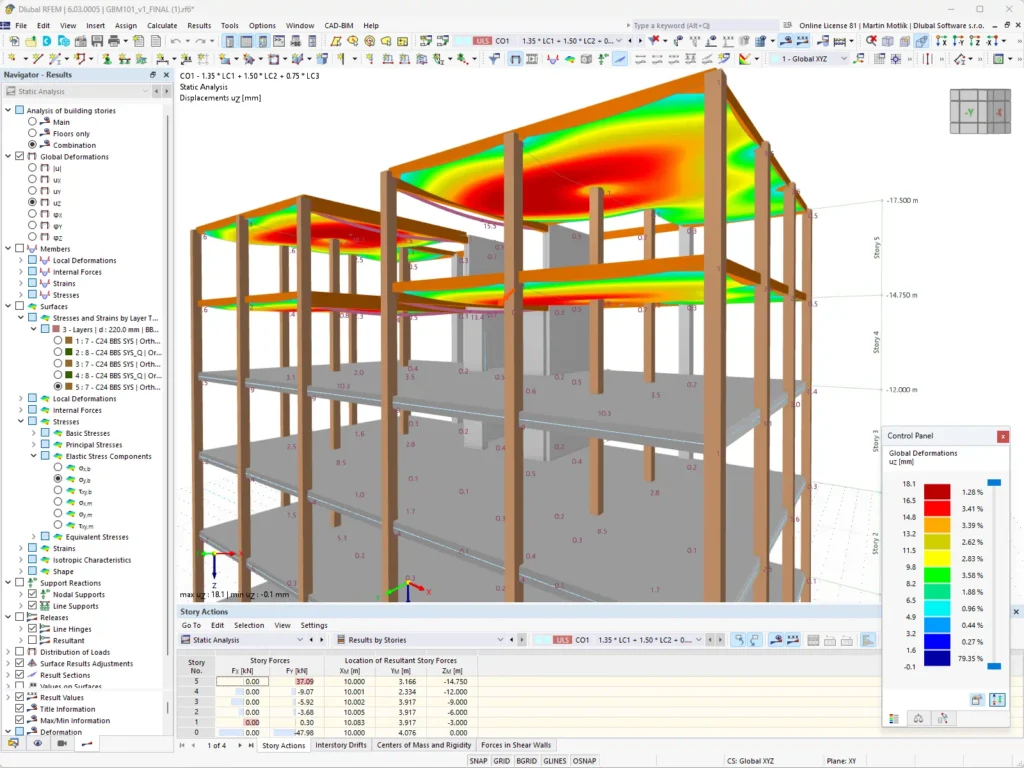
Tekla Structural Designer: Integrates with BIM for automation in structural analysis and design. By automating tasks such as load application and code checks, the tool improves the efficiency of the design process.
Automatic Documentation Generation
Revit: Offers automation in creating plans, sections, and elevations, maintaining consistency with the 3D model. The automatic synchronization of changes from the model to documentation ensures that drawings are always up-to-date.
Vectorworks: Uses automation to create construction documents efficiently. Its parametric approach and the ability to automatically link documentation to the BIM model facilitate the generation of detailed drawings.

ArchiCAD (Layout Book): Automates the generation of construction layouts through the Layout Book. Parametric model data is automatically updated in layouts, providing consistent and accurate documentation.
Dynamo: Dynamo automates repetitive tasks in the BIM process. Through visual scripting, users can create custom scripts to automate specific workflows, including documentation generation.

Energy Simulation and Sustainability
Green Building Studio: Automates energy simulations for sustainable performance analysis. Using BIM model data, the tool provides valuable information to optimize the project’s energy efficiency.
EnergyPlus: EnergyPlus automates advanced assessment of building energy consumption. Integrating with BIM, the tool allows accurate simulations to optimize the project’s energy performance.

DesignBuilder: Offers automation in thermal simulation and energy performance analysis. Its intuitive interface allows users to optimize the project for energy efficiency with ease.
IES VE: Uses automation for comprehensive energy performance and sustainability analyses. Integrating with BIM, the tool provides valuable insights to improve project efficiency and sustainability.

SimScale: Automatically performs fluid dynamics simulations and thermal analyses. Integrating with BIM, the tool offers automation in optimizing the design for thermal comfort and energy efficiency.
Transforming the Future of Construction with BIM Automation
BIM automation offers a diverse range of benefits, from time savings to reducing human errors. For beginners in this field, understanding the various available tools and how to integrate them into the BIM workflow is essential. By embracing automation, construction professionals can not only improve efficiency but also elevate the quality and accuracy of projects, contributing to a more sustainable and innovative industry. The transformation of the future of construction is intrinsically linked to the ability to make the most of the automation tools available in a dynamic BIM environment.



Deixe um comentário